Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in pregnancy-baseline omega-3 status and early preterm birth: exploratory analysis of a randomised controlled trial
BJOG . 2020 Jul;127(8):975-981. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.16168
L A Simmonds 1, T R Sullivan 1, M Skubisz 1 2, P F Middleton 1 3, K P Best 1 3, L N Yelland 1 4, J Quinlivan 5, S J Zhou 6, G Liu 1 6, A J McPhee 1 7, R A Gibson 1 6, M Makrides 1 3
Objective: To identify a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) biomarker able to detect which women with singleton pregnancies are most likely to benefit from omega-3 supplementation to reduce their risk of early preterm birth.
Design: Exploratory analysis of a randomised controlled trial.
Setting: Six Australian hospitals.
Population: Women with a singleton pregnancy enrolled in the ORIP trial.
Methods: Using maternal capillary whole blood collected ~14 weeks' gestation, the fatty acids in total blood lipids were quantified using gas chromatography. Interaction tests examined whether baseline PUFA status modified the effect of omega-3 supplementation on birth outcomes.
Main outcome measure: Early preterm birth (<34 weeks' gestation).
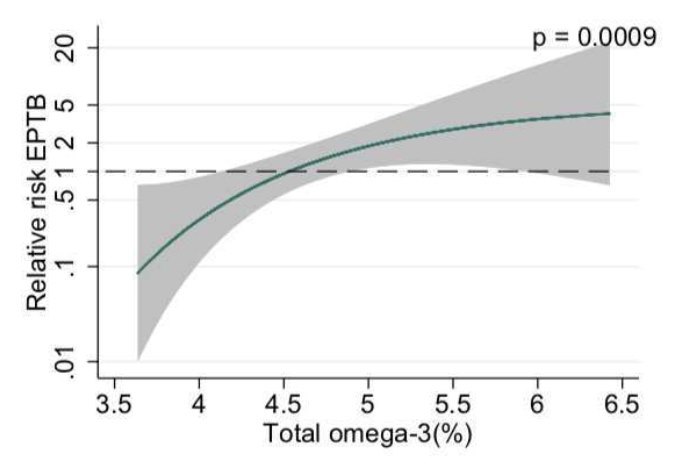
Results: A low total omega-3 PUFA status in early pregnancy was associated with a higher risk of early preterm birth. Among women with a total omega-3 status ≤4.1% of total fatty acids, omega-3 supplementation substantially reduced the risk of early preterm birth compared with control (0.73 versus 3.16%; relative risk = 0.23, 95% confidence interval CI 0.07-0.79). Conversely, women with higher total omega-3 status in early pregnancy were at lower risk of early preterm birth. Supplementing women with a baseline status above 4.9% increased early preterm birth (2.20 versus 0.97%; relative risk = 2.27, 95% CI 1.13-4.58).
Conclusions: Women with singleton pregnancies and low total omega-3 PUFA status early in pregnancy have an increased risk of early preterm birth and are most likely to benefit from omega-3 supplementation to reduce this risk. Women with higher total omega-3 status are at lower risk and additional omega-3 supplementation may increase their risk.
Download the PDF from VitaminDWiki
VitaminDWiki Omega-3 pages with PRETERM or PRE-TERM in title (13 as of Oct 2022)
This list is automatically updated
Items found: 17
|
Title |
|
Modified |
|
Preterm birth decreased by Omega-3, etc. - many studies |
|
01 Oct, 2024 |
|
Omega-3 fatty acid in pregnancy reduces risk of preterm and early preterm birth – Feb 2024 |
|
17 Aug, 2024 |
|
Omega-3 supplementation reduced preterm birth rate by 4X – RCT July 2020 |
|
21 Oct, 2022 |
|
Preterm birth might be prevented by Vitamin D, Omega-3, etc. (International survey) – Jan 2019 |
|
15 May, 2022 |
|
Preterm Births - promising preventions – anti-oxidants, Vitamin D, Omega-3, Zinc, etc. – Jan 2019 |
|
15 May, 2022 |
|
Preterm birth reduction by nutrients - Vitamin D is the best, Omega-3 is next best – May 2022 |
|
15 May, 2022 |
|
Preterm birth rate of pregnant smokers cut in half if take Omega-3 – RCT May 2017 |
|
20 Feb, 2022 |
|
Pre-term birth rate cut in half with 1000 milligrams of Omega-3 (if initially low) – RCT May 2021 |
|
04 Jun, 2021 |
|
Pregnant women in Australia to take Omega-3 when told of reduction in preterm births – Dec 2019 |
|
19 Nov, 2019 |
|
Preterm Births reduced by Omega-3, Zinc, and Vitamin D – Aug 2019 |
|
09 Aug, 2019 |
|
Preterm Births decreased by Omega-3 (analysis of 184 countries) – April 2019 |
|
27 Apr, 2019 |
|
Omega-3 index of 5 greatly decreases the risk of an early preterm birth – Dec 2018 |
|
04 Jan, 2019 |
|
Increasing Omega-3 reduces heart problems, autism, depression, preterm birth, breast cancer, etc. |
|
15 Dec, 2017 |
|
Preterm births strongly related to Vitamin D, Vitamin D Receptor, Iodine, Omega-3, etc |
|
13 Nov, 2017 |
|
Preterm birth extended by 2 weeks with Omega-3 – Meta-analysis Nov 2015 |
|
10 Dec, 2016 |
|
Omega-3 supplementation during pregnancy reduce early preterm births (save 1500 USD per child) – Aug 2016 |
|
12 Oct, 2016 |
|
Omega-3 helps pregnancy in many ways: preterm 26 percent less likely etc – review July 2012 |
|
08 Sep, 2015 |
VitaminDWiki Pregnancy pages with PRETERM of PRE-TERM in title (61 as of May 2022)
This list is automatically updated
Items found: 74
|
Title |
|
Modified |
|
Preterm birth risk increased 1.6 X if supplement with Calcium – Oct 2024 |
|
27 Dec, 2024 |
|
3X fewer preterm deliveries if take 2,000 IU of Vitamin D daily (small study, 9% refused) - Dec 2024 |
|
17 Dec, 2024 |
|
Vitamin D and pregnancy, preterm birth, preeclampsia - Whittle Nov 2024 |
|
24 Nov, 2024 |
|
Preterm birth decreased by Omega-3, etc. - many studies |
|
01 Oct, 2024 |
|
Preterm births appear reduced 34% by Vitamin D, 11% by Omega-3 - Jan 2021 |
|
01 Oct, 2024 |
|
Preterm births reduced by Vitamin D - many studies |
|
01 Oct, 2024 |
|
Pfizer’s RSV vaccine found to increase risk of preterm births by 24%, etc. – Sept 2024 |
|
29 Sep, 2024 |
|
Omega-3 fatty acid in pregnancy reduces risk of preterm and early preterm birth – Feb 2024 |
|
17 Aug, 2024 |
|
800 mg of Magnesium early in 3rd trimester significantly increased brain activity in preterm infants – RCT May 2024 |
|
03 Jun, 2024 |
|
Preterm birth rate increased in US but decreased in Finland (high Vitamin D) - Jan 2024 |
|
09 Feb, 2024 |
|
Preterm birth chance reduced –17P (expensive drug) or Vitamin D – June 2015 |
|
01 Jan, 2024 |
|
Preterm birth and low Vitamin D - many studies |
|
24 Dec, 2023 |
|
Preterm births are VERY costly – Feb 2017 |
|
24 Dec, 2023 |
|
Preterm birth cost for employers approximately 50,000 dollars – Oct 2017 |
|
24 Dec, 2023 |
|
Preterm Birth 2.7X more likely if low vitamin D (dark skin in this case) - Nov 2023 |
|
01 Nov, 2023 |
|
4.4 X more likely to have a preterm birth if low vitamin D while pregnant (India) - May 2022 |
|
01 Nov, 2023 |
|
Omega-3 supplementation reduced preterm birth rate by 4X – RCT July 2020 |
|
21 Oct, 2022 |
|
Arab preterm infants often have less than 10 ng of vitamin D - 2010 |
|
15 May, 2022 |
|
Preterm birth interventions – 4 studies found possible vitamin D benefit – Cochrane – Nov 2018 |
|
15 May, 2022 |
|
Preterm birth might be prevented by Vitamin D, Omega-3, etc. (International survey) – Jan 2019 |
|
15 May, 2022 |
|
Preterm Births - promising preventions – anti-oxidants, Vitamin D, Omega-3, Zinc, etc. – Jan 2019 |
|
15 May, 2022 |
|
Preterm birth reduction by nutrients - Vitamin D is the best, Omega-3 is next best – May 2022 |
|
15 May, 2022 |
|
Preterm birth rate of pregnant smokers cut in half if take Omega-3 – RCT May 2017 |
|
20 Feb, 2022 |
|
Preterm birth varies with season: 25 percent more likely if conception in autumn – Feb 2022 |
|
04 Feb, 2022 |
|
Pre-term birth rate cut in half with 1000 milligrams of Omega-3 (if initially low) – RCT May 2021 |
|
04 Jun, 2021 |
|
Preterm birth risk increased 16 pcnt if heat wave (perhaps outside less) - Nov 2020 |
|
16 Nov, 2020 |
|
Preterm birth associated with many genes, including the Vitamin D Receptor again – Jan 2020 |
|
30 Jan, 2020 |
|
Preterm birth 8X more likely if poor Vitamin D Receptor – Dec 2019 |
|
31 Dec, 2019 |
|
8 percent fewer preterm births if adequate Selenium from food – Aug 2019 |
|
24 Dec, 2019 |
|
Pregnant women in Australia to take Omega-3 when told of reduction in preterm births – Dec 2019 |
|
19 Nov, 2019 |
|
Preterm birth 9 X more likely if fetus had a poor Vitamin D Receptor and previous miscarriage – Aug 2017 |
|
12 Nov, 2019 |
|
Preterm birth rate not vary with vitamin D level (when all are less than 30 ng) – Oct 2019 |
|
17 Oct, 2019 |
|
Extreme preterm infants helped somewhat by 800 IU of vitamin D – RCT Jan 2018 |
|
01 Oct, 2019 |
|
Preterm Births reduced by Omega-3, Zinc, and Vitamin D – Aug 2019 |
|
09 Aug, 2019 |
|
Preterm birth increases risk of heart disease by 1.5 X by age 40 – June 2019 |
|
06 Aug, 2019 |
|
Preterm Births decreased by Omega-3 (analysis of 184 countries) – April 2019 |
|
27 Apr, 2019 |
|
Preterm birth 3X more likely if low vitamin D – Oct 2018 |
|
07 Feb, 2019 |
|
Omega-3 index of 5 greatly decreases the risk of an early preterm birth – Dec 2018 |
|
04 Jan, 2019 |
|
Preterm births 12 X more likely if poor Vitamin D Receptor (white infants in Italy) – meta-analysis Aug 2018 |
|
27 Aug, 2018 |
|
Third trimester Vitamin D levels were lower if pre-term labor was expected – March 2018 |
|
24 Mar, 2018 |
|
Preterm birth 4X more likely if very low Vitamin D (Chinese) - Feb 2018 |
|
28 Feb, 2018 |
|
Preterm birth rates increased in 15 European countries – Oct 2013 |
|
23 Dec, 2017 |
|
Vitamin D intervention reduces preterm births and low birth weight by 60 percent – Cochrane Reviews – Nov 2017 |
|
07 Dec, 2017 |
|
Preterm birth rate increased 60 percent in 50 years (US) |
|
26 Nov, 2017 |
|
Preterm births strongly related to Vitamin D, Vitamin D Receptor, Iodine, Omega-3, etc |
|
13 Nov, 2017 |
|
Vitamin D Receptor is associated with preeclampsia, gestational diabetes and preterm birth – Nov 2017 |
|
10 Nov, 2017 |
|
Preterm birth trend toward 2.5 X more likely if less than 10 ng of Vitamin D – Aug 2017 |
|
26 Aug, 2017 |
|
Preterm birth rate reduced by vitamin D – 78 percent if non-white, 39 percent if white – July 2017 |
|
27 Jul, 2017 |
|
Preterm birth more likely if dark skinned and low vitamin D (not white-skinned) – April 2017 |
|
06 Jul, 2017 |
|
Risk of preterm birth twice as likely when less than 10 ng of vitamin D – Nov 2016 |
|
13 Apr, 2017 |
|
Preterm labor 20 times more likely if low vitamin D, etc. (India) – Feb 2017 |
|
08 Mar, 2017 |
|
Preterm birth rate reduced by 43 percent with adequate Vitamin D supplementation – meta-analysis Feb 2017 |
|
02 Mar, 2017 |
|
Pre-term birth - many of risk factors are associated with low vitamin D |
|
27 Feb, 2017 |
|
Preterm birth rate reduced 57 percent by Vitamin D – Nov 2015 |
|
23 Jan, 2017 |
|
Vitamin D Webinar - cost of pre-term birth etc- Baggerly Nov 2013 |
|
11 Dec, 2016 |
|
Preterm birth extended by 2 weeks with Omega-3 – Meta-analysis Nov 2015 |
|
10 Dec, 2016 |
|
Omega-3 supplementation during pregnancy reduce early preterm births (save 1500 USD per child) – Aug 2016 |
|
12 Oct, 2016 |
|
Zinc helps pregnancies – 14 percent fewer preterm births, etc. – Cochrane RCT Feb 2015 |
|
14 Jun, 2016 |
|
Preterm birth has become the leading cause of infant mortality (vitamin D not mentioned) – JAMA June 2016 |
|
07 Jun, 2016 |
|
Preterm birth 30 percent more likely if low vitamin D – meta-analysis May 2016 |
|
20 May, 2016 |
|
Asthmatic pregnant women had 30 percent more preterm births if air pollution (vitamin D not mentioned) – March 2016 |
|
09 Mar, 2016 |
|
Omega-3 helps pregnancy in many ways: preterm 26 percent less likely etc – review July 2012 |
|
08 Sep, 2015 |
|
Extreme preterm survival 30 percent less likely if little sunshine 23-28 weeks – June 2015 |
|
05 Sep, 2015 |
|
Magnesium (Sulfate) reduces risk of cerebral palsy for those at risk of pre-term births – Dec 2013 |
|
18 Aug, 2015 |
|
Respiratory distress after preterm birth is more likely if low vitamin D – review April 2015 |
|
05 Aug, 2015 |
|
Pre-term births reduced in half if 40 ng of vitamin D in 3rd trimester – Nov 2014 |
|
15 Mar, 2015 |
|
Chance of preterm birth is strongly associated with low vitamin D – Feb 2015 |
|
05 Feb, 2015 |
|
The more preterm the birth, the lower the vitamin D level (both mothers and infants) – Feb 2014 |
|
05 Feb, 2015 |
|
Preterm infants more likely to have vitamin D levels below 20 ng – Feb 2014 |
|
05 Feb, 2015 |
|
Decreased risk of preterm birth if have more than 36 ng of vitamin D – Jan 2015 |
|
09 Jan, 2015 |
Cognitive 48, Pregnancy 39, Cardiovascular 32, Magnesium 31, Infant-Child 31, Depression 29, Meta-analysis 22, Zinc 22, Intervention 21, Inflammation 18, Sports 16, Vitamin K 15, Obesity 13, Trauma and surgery 12, Virus 12, Diabetes 11, Supplement 10, Multiple Sclerosis 9, Seniors 9, ADHD 9, Iron 9, Autism 8, Iodine 8, Vitamin B12, 8 Sleep 7, Women 7, Resveratrol 7, Boron 6, Cancer - Breast 6, Curcumin 6, Vitamin A 6, Liver 6, Cancer - Prostate 5, Vitamin C 5, Mortality 5, Antibiotics, probiotics 4, Hypertension 4, Veterinary 4, Cancer - after diagnosis 4, Rheumatoid Arthritis 4, Metabolic Syndrome 4